In modern electronics manufacturing, product quality and reliability are determined long before a device reaches the end user. One of the most critical stages in this journey is the SMT assembly process, where electronic components are mounted onto printed circuit boards with speed, precision, and repeatability.
For OEMs, hardware startups, and electronics buyers, understanding how the SMT assembly process works is essential. It not only explains how circuit boards are built, but also reveals where defects can occur, how quality is controlled, and what separates a capable SMT manufacturer from an unreliable one.
This article breaks down the SMT assembly process step by step and explains why it plays such a central role in modern electronics assembly and PCBA manufacturing.
What Is the SMT Assembly Process?
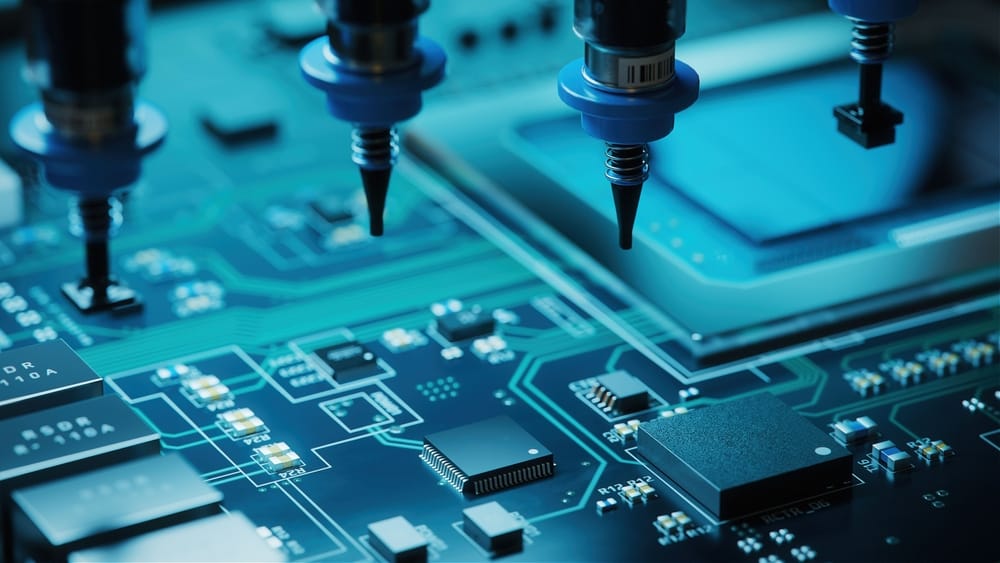
The SMT assembly process is the sequence of manufacturing steps used to place and solder surface mount components directly onto the surface of a PCB. It is a core part of SMT manufacturing and the most widely used assembly method in today’s electronics industry.
Unlike through-hole assembly, SMT assembly relies heavily on automated production lines. These lines are designed to handle small, densely packed components with high accuracy, making SMT ideal for compact, high-performance electronic products.
While SMT manufacturing refers to the broader production framework, the SMT assembly process focuses specifically on how components are applied, soldered, and inspected on the board.
Overview of the SMT Assembly Workflow
At a high level, the SMT assembly workflow follows a structured and repeatable path:
-
Solder paste printing
-
Component placement (pick-and-place)
-
Reflow soldering
-
Inspection and quality control
Each step builds on the previous one. A mistake early in the SMT assembly process can propagate downstream, leading to rework, yield loss, or field failures. This is why experienced manufacturers place strong emphasis on process control and automation throughout the SMT line.
Step-by-Step SMT Assembly Process
Solder Paste Printing
The SMT assembly process begins with solder paste printing. In this step, solder paste is applied to the PCB pads using a stainless steel stencil.
The purpose of solder paste printing is to deposit the correct amount of solder at precise locations. Too much paste can cause solder bridging, while too little can lead to weak or open joints.
Key factors in this stage include:
-
Stencil design and thickness
-
Paste viscosity and composition
-
Alignment accuracy
Many SMT lines use SPI (Solder Paste Inspection) immediately after printing to verify paste volume and alignment. For electronics buyers, the presence of SPI is often a strong indicator of a manufacturer’s quality mindset.
Pick-and-Place Component Assembly
Once solder paste is applied, the board moves to the pick-and-place stage. Automated machines pick surface mount components from feeders and place them onto the PCB at high speed.
Modern pick-and-place machines can place tens of thousands of components per hour with extremely tight tolerances. This level of precision is essential for fine-pitch components such as QFNs, BGAs, and small passive devices.
Critical aspects of this stage include:
-
Placement accuracy
-
Component orientation
-
Feeder setup and verification
Errors at this step can result in misaligned components or polarity issues, which may not always be visible without proper inspection.
Reflow Soldering
After component placement, the PCB enters the reflow soldering stage. The board passes through a reflow oven, where controlled heat melts the solder paste and forms permanent electrical and mechanical connections.
A properly controlled reflow profile is critical. Temperature ramps, soak time, peak temperature, and cooling rates all affect solder joint quality.
Common reflow-related issues include:
-
Cold solder joints
-
Tombstoning
-
Warpage or thermal stress
Experienced SMT manufacturers carefully develop and monitor reflow profiles to match specific board designs and component requirements.
Inspection and Quality Control
Inspection is a crucial part of the SMT assembly process. Even with advanced automation, inspection systems are needed to detect defects that could impact performance or reliability.
Common inspection methods include:
-
AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) for placement and solder joint verification
-
X-ray inspection for hidden joints such as BGAs
-
Visual inspection for special or low-volume builds
Effective inspection ensures that defects are detected early, reducing rework costs and preventing faulty boards from reaching final assembly or customers.
Common Challenges in the SMT Assembly Process

Despite its maturity, the SMT assembly process still presents challenges that require experience and process discipline to manage.
Typical issues include:
-
Solder bridging between fine-pitch pads
-
Tombstoning of small passive components
-
Component skew or misalignment
-
Insufficient solder volume
How a manufacturer identifies, analyzes, and prevents these issues says a great deal about their SMT capability. Buyers should look beyond defect rates and ask about root-cause analysis and continuous improvement practices.
How the SMT Assembly Process Impacts PCBA Quality and Reliability
The quality of the SMT assembly process directly affects overall PCBA performance. Poor solder joints or misaligned components can lead to intermittent failures, reduced product lifespan, and higher warranty costs.
A stable SMT assembly process improves:
-
Yield rates
-
Electrical performance
-
Long-term reliability
For products used in industrial, medical, or automotive applications, SMT process stability is often a non-negotiable requirement.
SMT Assembly Process for Prototype vs Mass Production
The SMT assembly process differs between prototype builds and high-volume production.
Prototype SMT assembly emphasizes:
-
Flexibility
-
Rapid changeovers
-
Engineering support
Mass production SMT assembly focuses on:
-
Line balancing
-
Automation efficiency
-
Consistent repeatability
Manufacturers that can support both scenarios provide significant value, especially for startups and OEMs scaling products from NPI to volume production.
What to Look for in a Reliable SMT Assembly Process
When evaluating an SMT assembly supplier, electronics buyers should look beyond basic capabilities.
Key indicators of a reliable SMT assembly process include:
-
Well-configured SMT lines with modern equipment
-
Clear process documentation and traceability
-
Robust inspection systems (SPI, AOI, X-ray where applicable)
-
Strong engineering and DFM support
Transparent communication and a structured approach to quality control are often just as important as machine specifications.
SMT Assembly Services at SHDC

Understanding the SMT assembly process is essential—but executing it consistently in real production environments requires experience, discipline, and strong process control. This is where choosing the right SMT assembly partner becomes critical.
SHDC provides professional SMT assembly services tailored to the needs of international customers, particularly US-based OEMs and product teams. With modern SMT production lines, automated inspection systems, and structured workflow management, SHDC supports the full SMT assembly process—from solder paste printing and pick-and-place to reflow soldering and final inspection.
What differentiates SHDC is not only equipment capability, but also its focus on engineering support and quality assurance. The company works closely with customers during prototype, NPI, and volume production stages to ensure stable processes, consistent PCBA quality, and smooth scalability. Clear communication, documented procedures, and traceable quality control help reduce manufacturing risk and shorten time to market.
By combining Vietnam’s growing electronics manufacturing ecosystem with a process-driven approach to SMT assembly, SHDC positions itself as a reliable SMT assembly partner for companies seeking a practical and resilient alternative in their global supply chains.
>>>Read more: Profile’s SHDC Company
Final Thoughts on the SMT Assembly Process
The SMT assembly process is far more than a sequence of machines placing components onto a board. It is a tightly controlled system that combines automation, engineering expertise, and quality management.
For electronics manufacturers and buyers, understanding the SMT assembly process provides valuable insight into how products are built, where risks exist, and how quality is ensured. A well-executed SMT assembly process not only improves product performance but also reduces long-term manufacturing risk.
As part of a broader SMT manufacturing strategy, mastering this process is essential for producing reliable, scalable, and competitive electronic products.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語

