In modern electronics manufacturing, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is no longer just about machines placing components on a PCB. As production scales, quality requirements tighten, and customers demand traceability, the way an SMT department is organized and managed becomes a critical success factor.
For U.S. companies outsourcing PCB assembly, understanding the SMT department process helps evaluate whether a manufacturer can deliver consistent quality, stable output, and long-term scalability—not just short-term capacity.
This article explains what an SMT department process is, how it works at the department level, and why effective management of SMT lines, people, and quality control matters in professional PCB assembly.
Why the SMT Department Process Matters in PCB Assembly
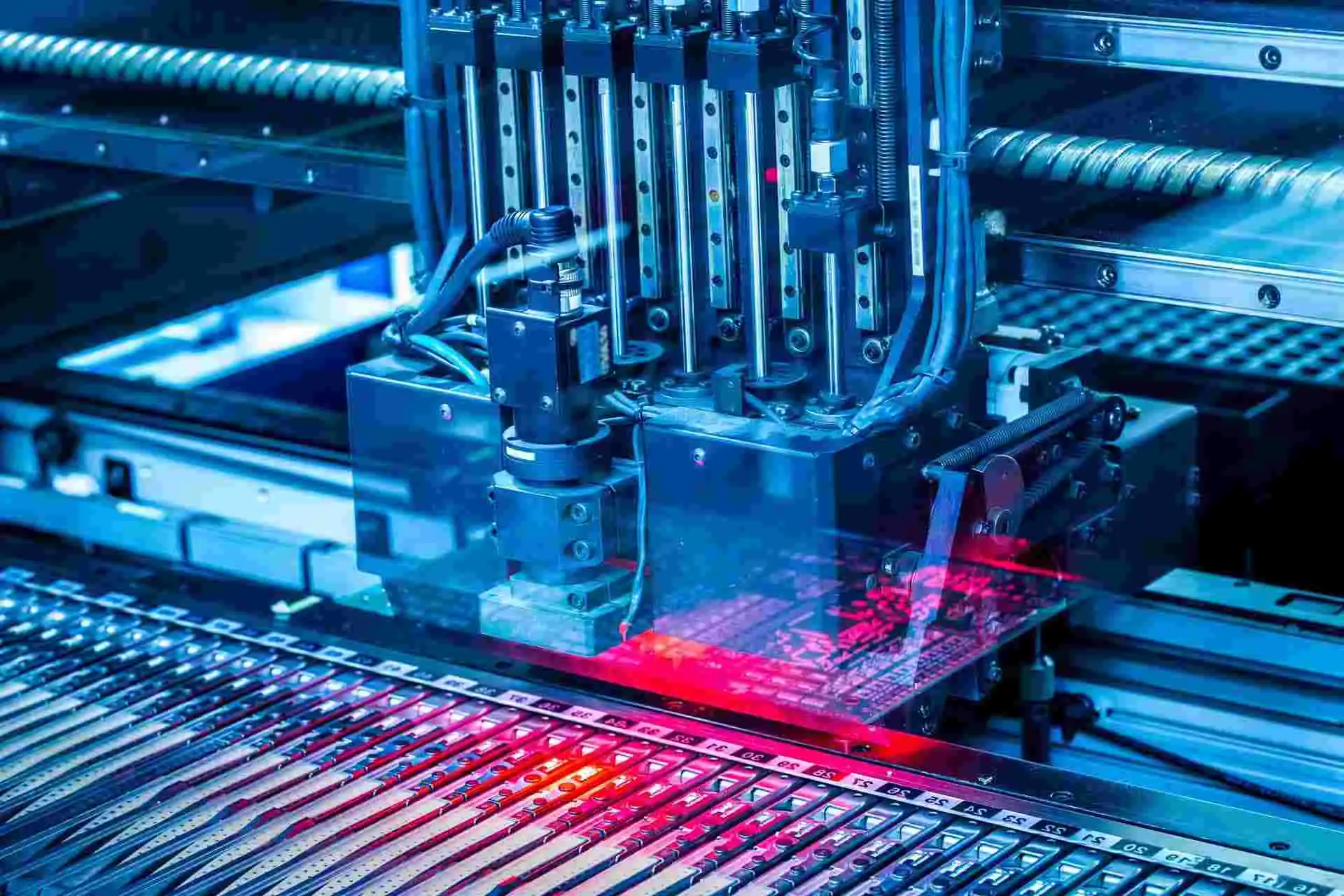
Many buyers focus on individual SMT lines: pick-and-place speed, reflow profiles, or AOI capability. However, in real manufacturing environments, problems rarely originate from a single machine. They arise from poor coordination across multiple lines, unclear responsibilities, or weak quality systems at the department level.
A well-defined SMT department process ensures:
-
Stable production across multiple SMT lines
-
Consistent quality regardless of shift or operator
-
Clear accountability for defects and corrective actions
-
Smooth coordination between engineering, production, and quality teams
Without strong SMT department management, even advanced equipment cannot prevent delays, repeated defects, or audit failures.
>>>Read more: What Is SMT Manufacturing and Why It Matters in Modern Electronics
What Is an SMT Department?
Definition of an SMT Production Department
An SMT department is the organizational unit within a PCB assembly factory responsible for all surface-mount operations. It oversees multiple SMT lines, operators, engineers, and quality personnel, managing the entire SMT stage of PCBA manufacturing.
It is important to distinguish between:
-
SMT line: A physical production line with printers, placement machines, reflow ovens, and inspection equipment
-
SMT department: The management structure that coordinates people, processes, equipment, and quality across all SMT lines
Core Responsibilities of an SMT Manufacturing Department
An SMT department typically handles:
-
Production planning and line allocation
-
Process control and parameter management
-
Operator training and supervision
-
In-process quality control and defect management
-
Coordination with engineering, materials, and downstream processes
This department-level oversight is what ensures consistency when production volume increases or product mix becomes complex.
SMT Department Structure: Roles and Team Organization
Key Roles Inside an SMT Department
A professionally run SMT department includes clearly defined roles, such as:
-
SMT Department Manager: Overall responsibility for output, quality, and efficiency
-
Process / Manufacturing Engineers: Define and optimize SMT processes
-
Line Leaders or Supervisors: Manage daily operations on each SMT line
-
SMT Operators: Execute production tasks according to work instructions
-
Quality Engineers / IPQC: Monitor in-process quality and enforce standards
-
Maintenance Technicians: Ensure equipment stability and uptime
Clear Responsibility Assignment
One common risk in SMT manufacturing is unclear ownership. A strong SMT department process clearly defines:
-
Who owns yield performance
-
Who has authority to stop a line when defects occur
-
Who performs root cause analysis and corrective actions
This clarity is essential for preventing repeated issues and maintaining customer confidence.
>>>Read more: SMT Assembly Process Explained: Step-by-Step Guide to Electronics Assembly 2026
Managing Multiple SMT Lines Within One Department

SMT Line Allocation Strategy
At the department level, managers decide how jobs are distributed across SMT lines based on:
-
Production volume
-
Board complexity
-
Component mix and feeder setup
-
Delivery deadlines
Some products run on dedicated lines, while others use flexible mixed-model lines. Effective SMT department management balances capacity while minimizing changeover time.
Production Scheduling and Coordination
The SMT department coordinates:
-
Production schedules across all lines
-
Material readiness and kitting
-
Engineering support during new product introduction (NPI)
This coordination prevents bottlenecks where one line is overloaded while another remains idle.
Changeover and Downtime Control
Changeovers are managed at the department level to:
-
Standardize setup procedures
-
Reduce downtime across all lines
-
Avoid errors caused by rushed transitions
Downtime is tracked not only per machine but across the entire SMT department to identify systemic issues.
SMT Department Process Flow (Department-Level View)
From a department perspective, the SMT process typically flows as follows:
-
Production order release and review
-
Line assignment and capacity planning
-
Material preparation and verification
-
SMT production execution across lines
-
In-process inspection and quality monitoring
-
Handoff to downstream processes (DIP, testing, final assembly)
This department-level view emphasizes coordination and control rather than individual machine steps.
SMT Quality Control Process at the Department Level

Quality Responsibilities of the SMT Department
The SMT department owns quality during the surface-mount stage, including:
-
First article inspection approval
-
In-process quality control (IPQC)
-
Defect tracking and yield monitoring
Quality is managed as a system, not as isolated inspections.
AOI, SPI, and Rework Management
Inspection data from SPI and AOI machines is collected and analyzed at the department level to:
-
Identify recurring defect patterns
-
Compare performance across SMT lines
-
Drive process improvements
Rework activities are controlled to prevent hidden quality risks.
Defect Escalation and Corrective Action
A robust SMT department process defines:
-
When a defect triggers line stoppage
-
How root cause analysis is conducted
-
How corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) are implemented
This structured approach aligns with IPC standards and ISO-based quality systems.
>>>Read more: SMT PCBA Process Explained: From Bare PCB to Reliable Electronic Assembly
Documentation, Traceability, and Compliance
Documentation is a cornerstone of SMT department management, especially for U.S. customers.
Typical controls include:
-
Standard work instructions (WI)
-
Process parameter records
-
Operator and line traceability
-
Lot-level and date-code tracking
These records support customer audits, regulatory compliance, and field failure investigations.
Common SMT Department Challenges and Solutions
Line Imbalance and Bottlenecks: Solved through better scheduling and capacity planning.
High Defect Rates Across Multiple Lines: Addressed with centralized defect analysis and standardized processes.
Operator Skill Gaps: Mitigated through structured training and cross-line certification.
Communication Gaps: Improved by clear interfaces between engineering, production, and quality teams.
Best Practices for Effective SMT Department Management
Leading SMT manufacturers follow best practices such as:
-
Standardizing processes across all SMT lines
-
Using data-driven performance metrics
-
Cross-training operators and supervisors
-
Conducting regular internal audits
-
Applying continuous improvement methodologies
These practices ensure long-term stability rather than short-term output gains.
SMT Department Process in Professional PCB Assembly Services

For U.S. companies outsourcing PCB assembly, a well-managed SMT department is a strong indicator of manufacturing maturity.
At SHDC, the SMT department is structured to manage multiple SMT lines with:
-
Clear role definitions
-
Standardized quality control processes
-
Full production and quality traceability
This department-level management enables SHDC to support both prototype and volume production while maintaining consistent quality for international customers.
FAQs
What is the role of an SMT department in PCB assembly?
It manages people, processes, and multiple SMT lines to ensure stable production and quality.
How is SMT department management different from SMT line management?
Line management focuses on equipment; department management focuses on coordination and system-level control.
Why is SMT department structure important for quality?
Clear structure ensures accountability, consistent processes, and effective defect prevention.
What standards apply to SMT department operations?
Common standards include IPC-A-610, ISO 9001, and customer-specific quality requirements.
How can buyers evaluate an SMT department?
By reviewing organization structure, quality systems, traceability, and audit readiness.
Conclusion
The SMT department process plays a decisive role in modern PCB assembly. By effectively managing SMT lines, people, and quality control, manufacturers can deliver consistent results, reduce risk, and scale production reliably.
For companies sourcing SMT services, evaluating the SMT department, not just the equipment, is essential to long-term manufacturing success.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語

