In electronics manufacturing, assembling components onto a board is only one part of the equation. What ultimately determines product reliability, yield, and scalability is the SMT PCBA process—the complete, controlled workflow that transforms a bare printed circuit board into a fully functional electronic assembly.
For US-based OEMs and product teams outsourcing electronics manufacturing, understanding the SMT PCBA process is critical. Many quality issues and field failures originate not from component defects, but from weaknesses in PCBA process control, inspection coverage, or engineering alignment during SMT production.
This article provides a detailed breakdown of the SMT PCBA process, explains how it differs from basic SMT assembly, and highlights what buyers should evaluate when selecting an SMT PCBA manufacturing partner.
What Is the SMT PCBA Process?
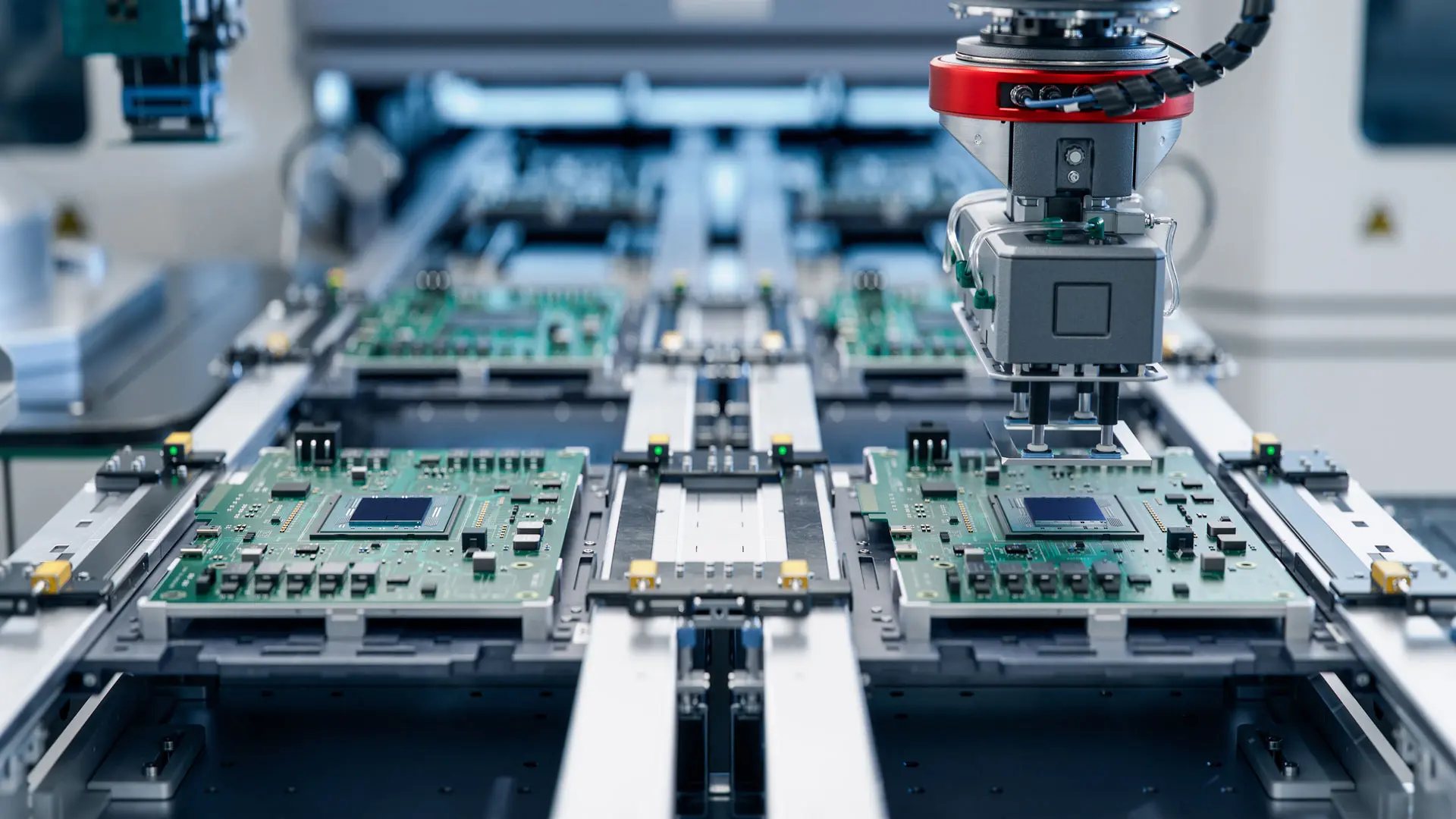
The SMT PCBA process refers to the end-to-end manufacturing sequence used to assemble surface-mount components onto a printed circuit board using Surface Mount Technology (SMT), followed by inspection, testing, and validation.
Unlike a single assembly step, the SMT PCBA process integrates:
-
Manufacturing data preparation
-
SMT assembly and soldering
-
Inspection and defect detection
-
Electrical and functional testing
-
Traceability, documentation, and packaging
A mature SMT PCBA process ensures that each board delivered is electrically functional, mechanically reliable, and repeatable at scale.
SMT Assembly vs. SMT PCBA Process: Key Differences
Although often used interchangeably, SMT assembly and the SMT PCBA process serve different purposes.
| SMT Assembly | SMT PCBA Process |
|---|---|
| Focuses on placing and soldering components | Covers the full manufacturing lifecycle |
| Ends after reflow soldering | Ends after inspection, testing, and validation |
| Equipment-centric | Process- and quality-centric |
| Suitable for basic builds | Required for reliable, scalable production |
For OEMs, the SMT PCBA process—not assembly speed alone—determines long-term product performance and manufacturing risk.
>>>Read more: SMT Assembly Process Explained: Step-by-Step Guide to Electronics Assembly 2026
Detailed Stages of the SMT PCBA Process
1. Engineering Review & Data Preparation
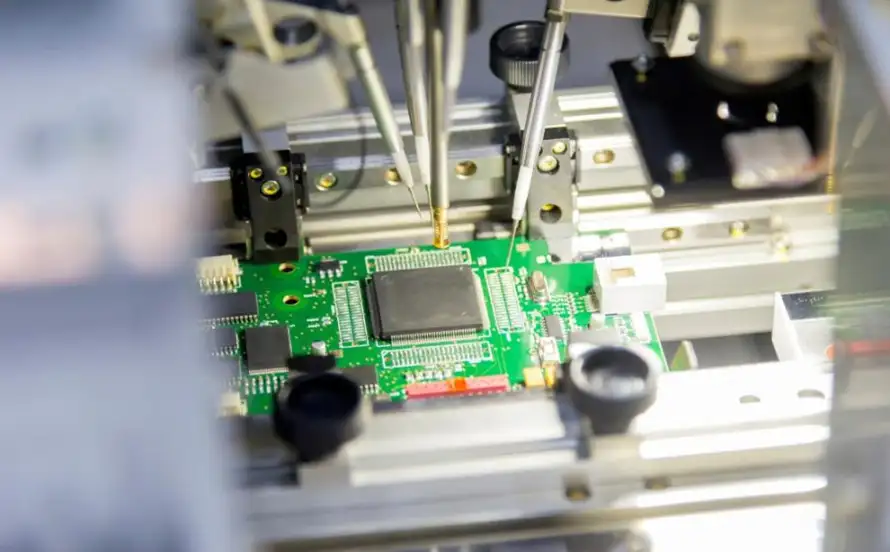
A reliable SMT PCBA manufacturing process begins with engineering validation. Before production, manufacturers review:
-
PCB Gerber files and stack-up
-
Bill of Materials (BOM)
-
Pick-and-place data
-
DFM/DFA requirements
This step helps identify soldering risks, footprint mismatches, polarity issues, and component availability concerns. Early engineering involvement significantly reduces rework and delays during SMT PCBA assembly.
2. Solder Paste Printing
Solder paste is applied to PCB pads using an automated stencil printer. Paste volume consistency is critical, as defects introduced here often propagate through the entire SMT PCBA process.
Process controls include:
-
Stencil design and thickness optimization
-
Printer alignment and pressure settings
-
Solder Paste Inspection (SPI)
High-quality SMT PCBA manufacturing relies on stable and repeatable paste printing.
3. SMT Component Placement
Pick-and-place machines accurately position surface-mount components onto the PCB. This stage defines both assembly efficiency and defect probability.
Critical factors include:
-
Placement accuracy
-
Feeder calibration
-
Component orientation and polarity
Errors at this stage increase rework rates and negatively impact PCBA yield.
4. Reflow Soldering
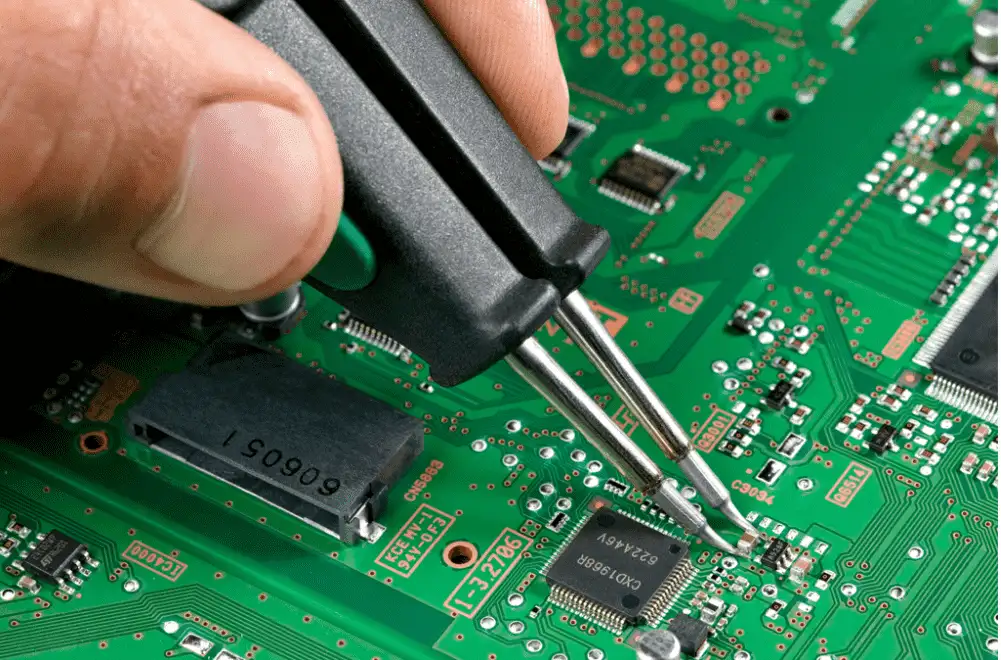

During reflow, the PCB passes through a temperature-controlled oven where solder paste melts and solidifies, forming permanent joints.
A controlled reflow profile:
-
Prevents solder bridges and tombstoning
-
Protects sensitive components
-
Ensures joint reliability over product life
Reflow stability is a core indicator of a mature SMT PCBA process.
5. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI systems inspect component placement, solder joints, and polarity after reflow. This step serves as a key quality gate in SMT PCBA assembly.
AOI helps detect:
-
Missing or misaligned components
-
Insufficient or excessive solder
-
Visual defects before electrical testing
>>>Read more: What Is SMT Manufacturing and Why It Matters in Modern Electronics
6. Through-Hole Assembly & Secondary Processes
Some designs require connectors, power components, or mechanical parts that cannot be mounted via SMT. These are added through selective soldering or manual processes and integrated into the SMT PCBA workflow.
Process alignment between SMT and secondary operations is critical for complex PCBAs.
7. Electrical & Functional Testing
Testing verifies that the SMT PCBA performs as designed. Depending on the product, testing may include:
-
In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
-
Functional test fixtures
-
Power, signal, and communication validation
Testing transforms assembly quality into verified product functionality.
8. Final Inspection, Traceability & Packaging
Completed PCBAs undergo final inspection, documentation, and traceability recording. Serial tracking, test records, and process documentation support warranty analysis and regulatory compliance.
This final stage ensures that SMT PCBA manufacturing meets both technical and commercial expectations.
Why the SMT PCBA Process Matters for OEMs

For US companies outsourcing electronics manufacturing, the most common risks include:
-
Inconsistent process execution
-
Limited inspection or testing coverage
-
Poor communication during NPI and scaling
A well-defined SMT PCBA process reduces:
-
Field failures
-
Production delays
-
Quality disputes
-
Total cost of ownership
Process maturity often matters more than equipment brand or line speed.
SMT PCBA Manufacturing in Vietnam
Vietnam has become a competitive location for SMT PCBA manufacturing, offering:
-
Cost efficiency
-
Skilled technical labor
-
Improving quality systems and infrastructure
For US companies diversifying supply chains, Vietnam presents a practical alternative—especially when working with manufacturers that operate structured, export-oriented SMT PCBA processes.
SMT PCBA Services at SHDC
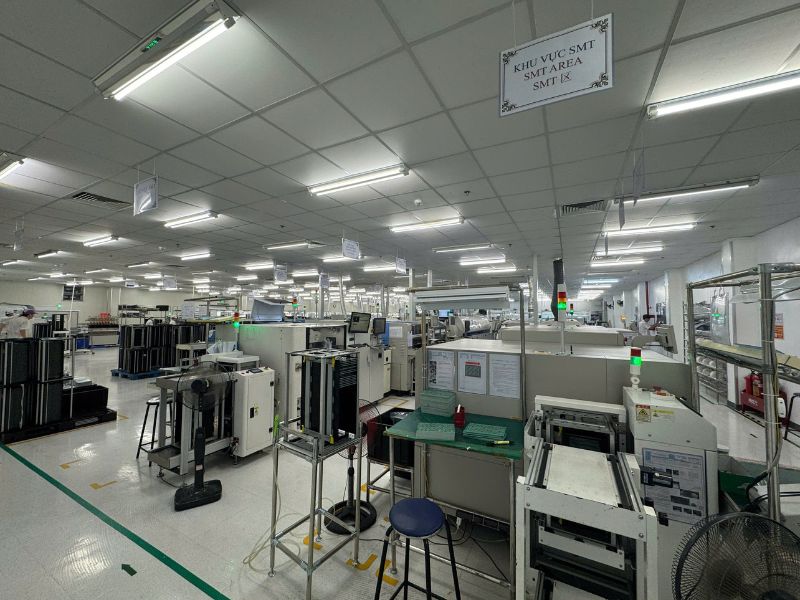

Executing a reliable SMT PCBA process requires engineering discipline, inspection coverage, and consistent communication.
SHDC provides SMT PCBA services for international customers, supporting prototype, NPI, and scalable production. With modern SMT lines, automated inspection systems, and process-driven manufacturing controls, SHDC manages each stage of the SMT PCBA process with accuracy and repeatability.
By combining Vietnam-based manufacturing advantages with structured PCBA process management, SHDC supports US OEMs seeking reliable SMT PCBA production with reduced supply chain risk.
>>>Read more: Profile’s SHDC Company
FAQs
What does SMT PCBA stand for?
SMT PCBA stands for Surface Mount Technology Printed Circuit Board Assembly, referring to the process of assembling surface-mount components onto a PCB and verifying its functionality.
What is the difference between SMT assembly and SMT PCBA process?
SMT assembly focuses on component placement and soldering, while the SMT PCBA process includes inspection, testing, validation, and quality control required for reliable production.
Why is the SMT PCBA process important?
A controlled SMT PCBA process reduces defects, improves yield, ensures product reliability, and supports scalable manufacturing.
What inspections are used in the SMT PCBA process?
Common inspections include SPI, AOI, and electrical or functional testing, depending on product complexity.
Is Vietnam suitable for SMT PCBA manufacturing?
Yes. Vietnam offers cost efficiency, skilled labor, and growing electronics manufacturing capabilities, making it a viable option for SMT PCBA outsourcing.
How do I choose a reliable SMT PCBA partner?
Evaluate engineering involvement, inspection coverage, process documentation, scalability, and communication—not just equipment or pricing.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語

